| CAS
NO. |
61-78-9 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
200-518-9 |
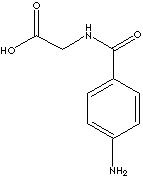
| FORMULA |
C9H10N2O3 |
| MOL
WT. |
194.19 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
SMILES |
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
para-Amino Hippuric acid;
|
| n-(4-Aminobenzoyl)-Glycine;
n-(p-Aminobenzoyl) Aminoacetic
Acid; p-Aminohippuric Acid; PAH; PAHA; |
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
light
yellow powder |
| MELTING POINT |
199 - 200 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
slightly soluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. Light sensitive |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
|
Hippuric Acid,
also called benzoylglycine and urobenzoic acid, ,
an analogue of amino acid
glycine. It is excreted from the urine of
domestic animals and other herbivorae but rarely found in human urine.
It is a crystallizable acid; soluble in hot water; melt point
187 C. It is hydrolysed at melting point and in caustic alkalis to benzoic acid and glycine.
It is synthesized as the intermediate for the manufacturing medicine (especially for urinary system)
and other
organic compounds. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
light
yellow powder |
|
ASSAY |
99.0%
min |
|
MELTING POINT |
199 - 200 C |
|
SULFATE |
0.1%
max
|
|
HEAVY
METALS |
20ppm
max
|
|
LOSS
ON DRYING
|
0.3%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: , Safety
Phrases: 22-24/25 |
